9.5. Developing Ethernet based applications with Linux + RTOS¶
9.5.1. Introduction¶
Common Port Switch (CPSW) provides Ethernet packet communication for the device & also acts as an Ethernet switch. The total ports includes the following:
Internal Host Port which provides the packet streaming interface to the device cores
External MAC Ports supporting the following:
Media Independent Interface (MII)
Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII)
Reduced Media Independent Interface (RMII)
Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII)
Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface (SGMII)
Quad Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface (QSGMII)
The MII modes supported vary based on device variant.
J721E has 2 instances
2-port (CPSW2G) in MCU domain (MCU_CPSW0)
9-port (CPSW9G) switch (MAIN_CPSW1) in main domain.
Note
CPSW instance is commonly referred with number of ports suffixed to the CPSW. 2, 5, and 9 port instances are referred to as CPSW2G, CPSW5G, and CPSW9G, respectively.
9.5.2. CPSW Support Software¶
Ethernet firmware (EthFw) is software running on main domain R5 for control and configuration of CPSW9G instance. As CPSW9G is a shared resource, the EthFw co-ordinates and manages resources between these cores and facilitates the configuration using Enet LLD.
Enet LLD is low level driver residing in the PDK. It supports CPSW2G and CPSW9G IPs and provides HAL layer for higher level stacks. EthFw uses Enet LLD for CPSW9G switch configuration.
TCP/IP Stack - lwIP stack is the only TCP/IP stack supported starting with SDK 8.1.
lwIP network interface driver (lwipif) is adaptation layer connecting Enet LLD to lwIP stack. This lwIP adaptation layer is part of Enet LLD and enables using CPSW2G and CPSW9G with lwIP TCP/IP applications.
gPTP Stack - PDK includes gPTP stack used mainly to validate and demonstrate time synchronization integration with CPSW.
Virtual CPSW MAC driver which implements standard Linux netdev interface and uses RPC services provided by rpmsg-kdrv Eth switch device which provides RPC interface to the Eth switch firmware running on the one of R5F cores and fully controls CPSW9G hardware module. The name of this virtual CPSW MAC driver is j721e_virt_mac.
Supported features:
ifconfig dev up/down
ifconfig dev <IP>
ifconfig dev hw ether <MAC> – only when interface is down
ethtool -k dev
The following block diagram shows the relevant components of the Ethernet Firmware which runs on the Main R5F core.
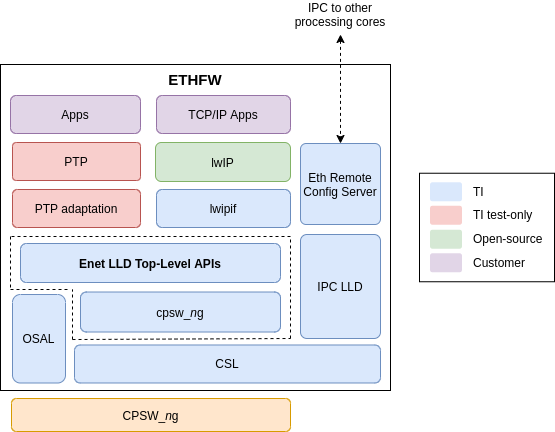
The scope of this developer note is to point to various documentation and source code resources available within the SDK (RTOS and Linux) to understand and use CPSW2G using Enet LLD & CPSW9G using EthFw in a user application.
9.5.3. Documentation References¶
SDK Component |
Documentation |
Description |
Section |
|---|---|---|---|
EthFw |
EthFw introduction and architecture review |
EthFw training |
|
EthFw |
EthFw API guide |
API guide |
|
EthFw |
EthFw user guide |
User guide |
|
EthFw |
EthFw demos |
Demos user guide |
|
PDK |
Enet API guide |
Enet Driver |
|
PDK |
Enet Module User’s Guide - driver, examples |
Full document |
|
PDK |
Enet Integration Guide - further details about Enet LLD initialization |
Full document |
|
PDK |
lwIP network interface User’s Guide and Migration Guide |
Full document |
|
PDK |
PHY integration guide - to help integrating new PHY with Enet LLD |
Implementing a New PHY Driver |
|
PDK |
Link Configuration Guidelines |
Link Configuration Guidelines |
|
PSDK LINUX |
${PSDK_LINUX_PATH}/docs/linux/index.html |
CPSW9G virtual mac driver user guide |
Foundational Components > Kernel > Kernel Drivers |
9.5.4. Source Code References¶
9.5.4.1. Enet LLD¶
SDK Component |
File / Folder |
Description |
|---|---|---|
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/enet.h |
Enet LLD interface for CPSW2G and CPSW9G |
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/include/phy/enetphy.h |
PHY LLD driver interface |
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/lwipif/inc/lwipif2enet_appif.h |
App interface of the Enet-based lwIP network interface driver |
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/board/ |
Board drivers for CPSW9G GESI board |
9.5.4.2. lwIP¶
SDK Component |
File / Folder |
Description |
|---|---|---|
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/transport/lwip/lwip-stack/src/include |
lwIP TCP/IP header files |
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/transport/lwip/lwip-contrib/apps |
lwIP contrib application header files |
9.5.4.3. EthFw¶
SDK Component |
File / Folder |
Description |
|---|---|---|
EthFw |
ethfw/ethremotecfg/protocol/rpmsg-kdrv-transport-ethswitch.h |
EthFw remote config protocol interface |
EthFw |
ethfw/ethremotecfg/server/include/ethremotecfg_server.h |
EthFw RTOS configuration server interface |
EthFw |
ethfw/ethremotecfg/client/include/ethremotecfg_client.h |
EthFw RTOS configuration client interface |
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/enet_cfgserver/enet_cfgserver.h |
CPSW configuration tool (GUI) interface |
9.5.4.4. Platform CPSW Virtual MAC¶
SDK Component |
File / Folder |
Description |
|---|---|---|
PSDK_LINUX |
${PSDK_LINUX_KERNEL_PATH}/drivers/net/ethernet/ti/j721e-cpsw-virt-mac.c |
J721E CPSW Virtual MAC driver |
9.5.4.5. Demo applications for EthFw¶
SDK Component |
File / Folder |
Decription |
|---|---|---|
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/examples/enet_loopback_test |
CPSW2G/9G internal loopback example on all supported cores (mcu2_0, mcu1_0, mcu2_1) |
PDK |
pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/examples/enet_lwip_example |
lwIP integration example for CPSW2G/9G. Supported core (mcu2_0, mcu1_0, mcu2_1) |
EthFw |
ethfw/apps/app_remoteswitchcfg_server |
This is switch Firmware. Hosts EthFw resource manager & remote config library. Also runs cpsw config tool server. |
EthFw |
ethfw/apps/app_remoteswitchcfg_client |
EthFw remote client on mcu2_1. Uses remote client to communicate to EthFw and get CPSW9G resources allocated to mcu2_1 |
9.5.5. EthFw boot flow¶
In PSDK LINUX and PSDK RTOS when Linux is used on A72, R5 SPL (tiboot3.bin) loads EthFw (/lib/firmware/j7-main-r5f0_0-fw). Linux Kernel late attaches with EthFw via remote proc.
In PSDK RTOS, EthFw running on mcu2_0 can also be booted by TI SBL.
9.5.6. Getting started on CPSW & EthFw¶
Refer to Enet module documentation [LINK] for information about Enet LLD key APIs and the Examples section for available examples on this platform.
Refer to Enet LLD integration guide [LINK] for a further details about the initialization of an Ethernet peripheral via Enet LLD.
9.5.6.1. Configuring Ethernet port mode¶
Based on your board configuration, port can be in RMII, RGMII etc. mode. You need to do below to configure port in required mode.
Configure port ENET control to required mode using board library.
Configure CPSW interface.
For RMII, it should be configured to below:
interface->layerType = ENET_MAC_LAYER_MII; interface->sublayerType = ENET_MAC_SUBLAYER_REDUCED; interface->variantType = ENET_MAC_VARIANT_NONE;
For RGMII, it should be configured to below:
interface->layerType = ENET_MAC_LAYER_GMII; interface->sublayerType = ENET_MAC_SUBLAYER_REDUCED; interface->variantType = ENET_MAC_VARIANT_NONE;
For SGMII (1Gbps) or XAUI (2.5Gbps), it should be configured to below:
interface->layerType = ENET_MAC_LAYER_GMII; interface->sublayerType = ENET_MAC_SUBLAYER_SERIAL; interface->variantType = ENET_MAC_VARIANT_NONE;
For USXGMII (5 or 10Gbps) on the supported SoCs, it should be configured to below:
interface->layerType = ENET_MAC_LAYER_XGMII; interface->sublayerType = ENET_MAC_SUBLAYER_SERIAL; interface->variantType = ENET_MAC_VARIANT_NONE;
9.5.6.2. Run Enet loopback example¶
We recommend running Enet loopback example first as this doesn’t have any dependency on board/EVM set up
See PDK user guide [LINK], section Build Steps for build steps
9.5.6.3. Run Enet lwIP example (TCP/IP example)¶
Once loopback example is run, you can run enet_lwip_example which uses lwIP stack for TCP/IP applications.
You need to connect EVM to PC running DHCP server. You should see IP printed on UART after running the example. The PDK Enet examples uses UART based on core it is running. Refer to PDK documentation for core-to-UART mapping. If you want to use static IP configuration, edit enet_lwip_example/lwipcfg.h to enable static IP.
You can ping to board using this IP address
You can also run iperf2 test (Enet LLD app is server, external PC is client).
9.5.6.4. Integrate new PHY in Enet¶
You need to add new PHY driver if existing PHY drivers present in enet/src/phy/* does not support PHY present on your Board.
Refer to PHY integration guide [LINK] which has details for adding support for new PHY in Enet LLD.
9.5.6.5. Modify the examples to support your board configuration¶
Modify examples to change PHY address, speed (10M/100M/1G etc.) setting, mode (RMII/RGMII etc.) settings.
Rebuild the example and run on your board. You should be able to see data transfer happening.
9.5.6.6. Use of GEL files for debug and diagnostics¶
Enet LLD includes debug and diagnostics gel files to help in integrating the CPSW in your app.
The gel files are present in the pdk/packages/ti/drv/enet/tools/debug_gels
cpsw_stats_print_regs.gel - prints non-zero statistics for CPSW
cpsw_mdio_config.gel - can be used to read/write PHY registers
cpsw_ale_print_table.gel - prints all entries of ALE table
cpsw_enetctrl_cfg.gel - makes sure that board mode matches the configured mode.
9.5.6.7. Using Linux Platform Virtual MAC¶
The virtual mac driver on Linux is auto loaded during the kernel boot. It is currently configured in DHCP mode so it acquires an IP via DHCP server running on PC connected to CPSW9G ports. To get an IP address of virtual mac driver, run “ifconfig”:
root@j7-evm:~# ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 50:51:A9:FB:F4:2E
inet addr:172.24.190.24 Bcast:172.24.191.255 Mask:255.255.252.0
inet6 addr: fe80::5251:a9ff:fefb:f42e/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:1327 errors:0 dropped:120 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:215 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:177194 (173.0 KiB) TX bytes:21218 (20.7 KiB)
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 70:FF:76:1D:87:95
inet addr:192.168.1.31 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::72ff:76ff:fe1d:8795/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:2 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:56 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:684 (684.0 B) TX bytes:10769 (10.5 KiB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:2 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:2 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:140 (140.0 B) TX bytes:140 (140.0 B)
Below standard Linux command can be run on the virtual mac interface.
ifconfig dev up/down
ifconfig dev <IP>
ifconfig dev hw ether <MAC> – only when interface is down
ethtool -k dev
