3.2.4.16. MMC/SD¶
3.2.4.16.1. Introduction¶
The multimedia card high-speed/SDIO (MMC/SDIO) host controller provides an interface between a local host (LH) such as a microprocessor unit (MPU) or digital signal processor (DSP) and either MMC, SD® memory cards, or SDIO cards and handles MMC/SDIO transactions with minimal LH intervention.
Main features of the MMC/SDIO host controllers:
- Full compliance with MMC/SD command/response sets as defined in the Specification.
- Support:
- 4-bit transfer mode specifications for SD and SDIO cards
- 8-bit transfer mode specifications for eMMC
- Built-in 1024-byte buffer for read or write
- 32-bit-wide access bus to maximize bus throughput
- Single interrupt line for multiple interrupt source events
- Two slave DMA channels (1 for TX, 1 for RX)
- Designed for low power and programmable clock generation
- Maximum operating frequency of 48MHz
- MMC/SD card hot insertion and removal
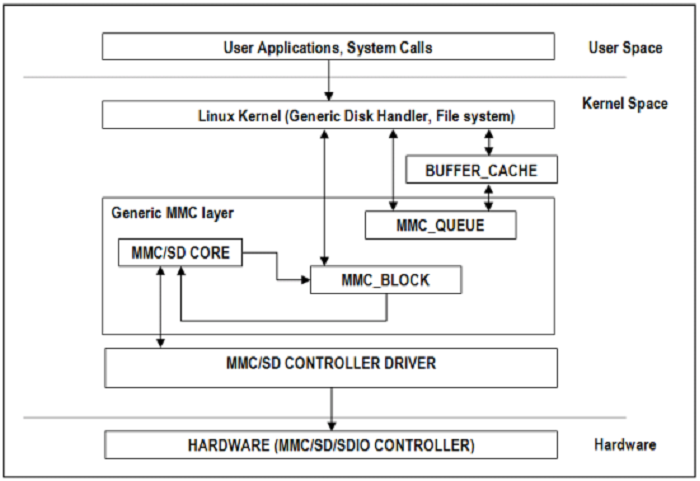
MMC/SD Driver Architecture
3.2.4.16.2. References¶
- JEDEC eMMC Homepage [http://www.jedec.org/category/technology-focus-area/flash-memory-ssds-ufs-emmc]
- SD ORG Homepage [http://www.sdcard.org]
3.2.4.16.3. Acronyms & Definitions¶
| Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|
| MMC | Multimedia Card |
| HS-MMC | High Speed MMC |
| SD | Secure Digital |
| SDHC | SD High Capacity |
| SDIO | SD Input/Output |
Table: MMC/SD: Acronyms
3.2.4.16.4. Features¶
The SD driver supports the following features:
- The driver is built in-kernel (part of vmlinux)
- SD cards including SD High Speed and SDHC cards
- Uses block bounce buffer to aggregate scattered blocks
3.2.4.16.5. Supported High Speed Modes¶
3.2.4.16.6. Driver Configuration¶
The default kernel configuration enables support for MMC/SD(built-in to kernel).
The selection of MMC/SD/SDIO driver can be modified using the linux kernel configuration tool. Launch it by the following command:
$ make menuconfig ARCH=arm
Building into Kernel
- Ensure that the following config options are set to ‘y’:
- CONFIG_MMC
- CONFIG_MMC_BLOCK
- CONFIG_MMC_SDHCI
- CONFIG_MMC_SDHCI_OMAP (for DRA7XX and AM57XX devices)
- CONFIG_MMC_OMAP (for AM335X and AM437X devices)
Building as Loadable Kernel Module
Depending on your configuration, any of the above options can be set to ‘m’ to build them as a module. Use the following command to install all modules tp your filesystem.
# sudo -E make modules_install ARCH=arm INSTALL_MOD_PATH=path/to/filesystem
Boot the kernel upto kernel prompt and use modprobe to insert the driver module and all its dependencies.
# modprobe sdhci-omap (for DRA7XX and AM57XX devices)
# modprobe omap_hsmmc (for AM335X and AM437X devices)
If ‘udev’ is running and the SD card is already inserted, the devices nodes will be created and filesystem will be automatically mounted if exists on the card.
Enabling eMMC Card Background operations support
This can be done using the “mmc-utils” tool from user space or using the “mmc” command in U-boot.
Command to enable bkops from userspace using mmc-utils, assuming eMMC instance to be mmcblk0
root@dra7xx-evm:mmc bkops enable /dev/mmcblk0
You can find the instance of eMMC by reading the ios timing spec form debugfs
root@dra7xx-evm:~# cat /sys/kernel/debug/mmc0/ios
----
timing spec: 9 (mmc HS200)
---
or by looking for boot partitions, eMMC has two bootpartitions mmcblk<x>boot0 and mmcblk<x>boot1
root@dra7xx-evm:/# ls /dev/mmcblk*boot*
/dev/mmcblk0boot0 /dev/mmcblk0boot1
| FUNCTIONAL UHS CARDS |
|---|
| ATP 32GB UHS CARD AF32GUD3 |
| STRONTIUM NITRO 466x UHS CARD |
| SANDISK EXTREME UHS CARD |
| SANDISK ULTRA UHS CARD |
| SAMSUNG EVO+ UHS CARD |
| SAMSUNG EVO UHS CARD |
| KINGSTON UHS CARD (DDR mode) |
| TRANSCEND PREMIUM 400X UHS CARD (Non fatal error and then it re-enumerates in UHS mode) |
| FUNCTIONAL (WITH LIMITED CAPABILITY) UHS CARD |
|---|
| SONY UHS CARD - Voltage switching fails and enumerates in high speed |
| GSKILL UHS CARD - Voltage switching fails and enumerates in high speed |
| PATRIOT 8G UHS CARD - Voltage switching fails and enumerates in high speed |
