Data Flows¶
The app_edgeai application at a high level can be split into 3 parts,
Input pipeline - Grabs a frame from camera, video, image or RTSP source
Output pipeline - Sends the output to display or a file
Compute pipeline - Performs pre-processing, inference and post-processing
Here are the data flows for each reference demo and the corresponding GStreamer launch strings that app_edgeai application generates. User can interact with the application via the Demo Configuration file
Image classification¶
In this demo, a frame is grabbed from an input source and split into two paths. The “analytics” path resizes the input maintaining the aspect ratio and crops the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The “visualization” path is provided to the post-processing module which overlays the detected classes. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
v4l2src device=/dev/video2 io-mode=2 ! image/jpeg, width=1280, height=720 ! jpegdec ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=454, height=256 ! tiovxcolorconvert out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! videobox left=115 right=115 top=16 bottom=16 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=0 mean-0=123.675000 mean-1=116.280000 mean-2=103.530000 scale-0=0.017000 scale-1=0.018000 scale-2=0.017000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=1280, height=720 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
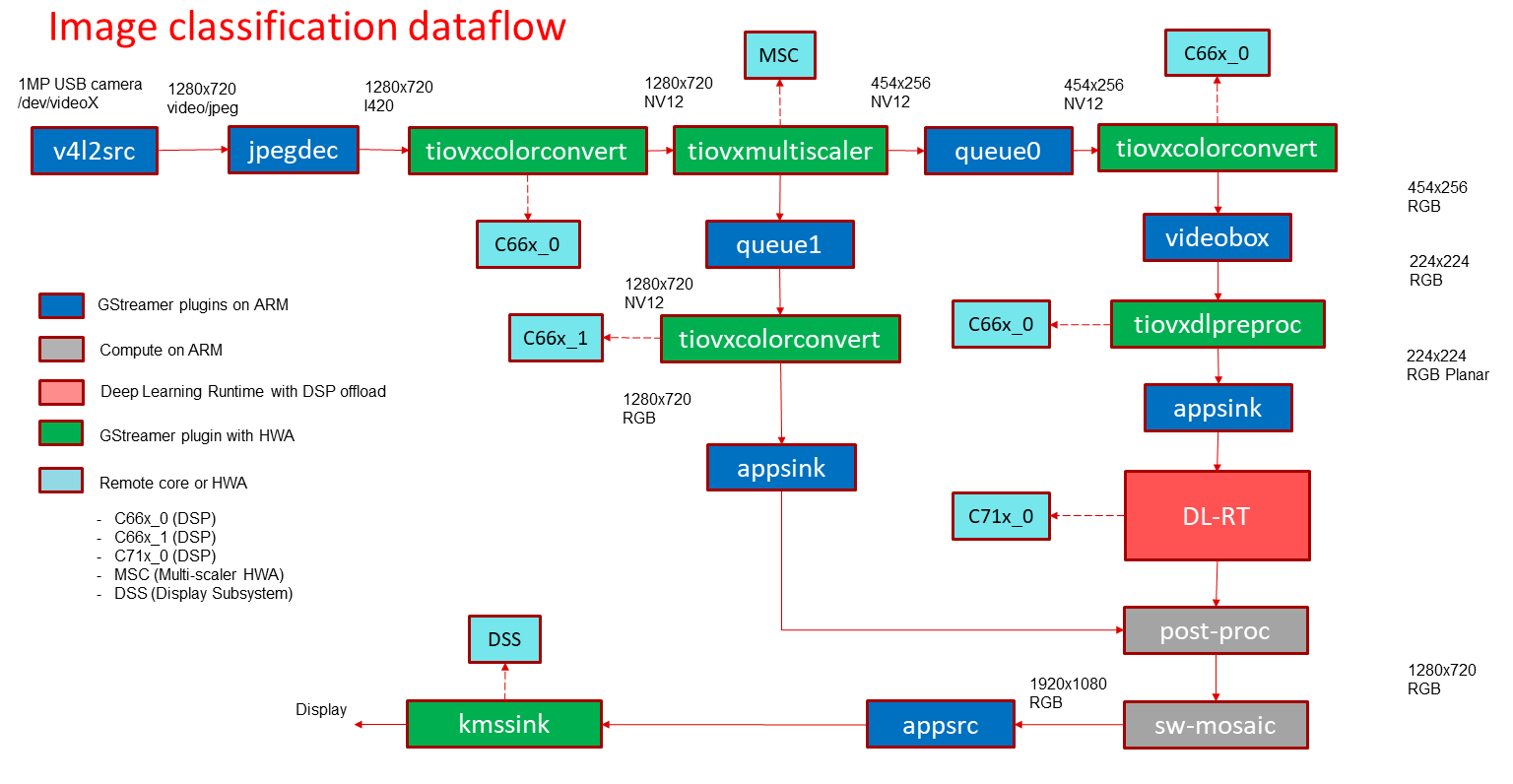
Fig. 14 GStreamer based data-flow pipeline for image classification demo with USB camera and display¶
Object Detection¶
In this demo, a frame is grabbed from an input source and split into two paths. The “analytics” path resizes the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The “visualization” path is provided to the post-processing module which overlays rectangles around detected objects. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
v4l2src device=/dev/video2 io-mode=2 ! image/jpeg, width=1280, height=720 ! jpegdec ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=320, height=320 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=1280, height=720 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
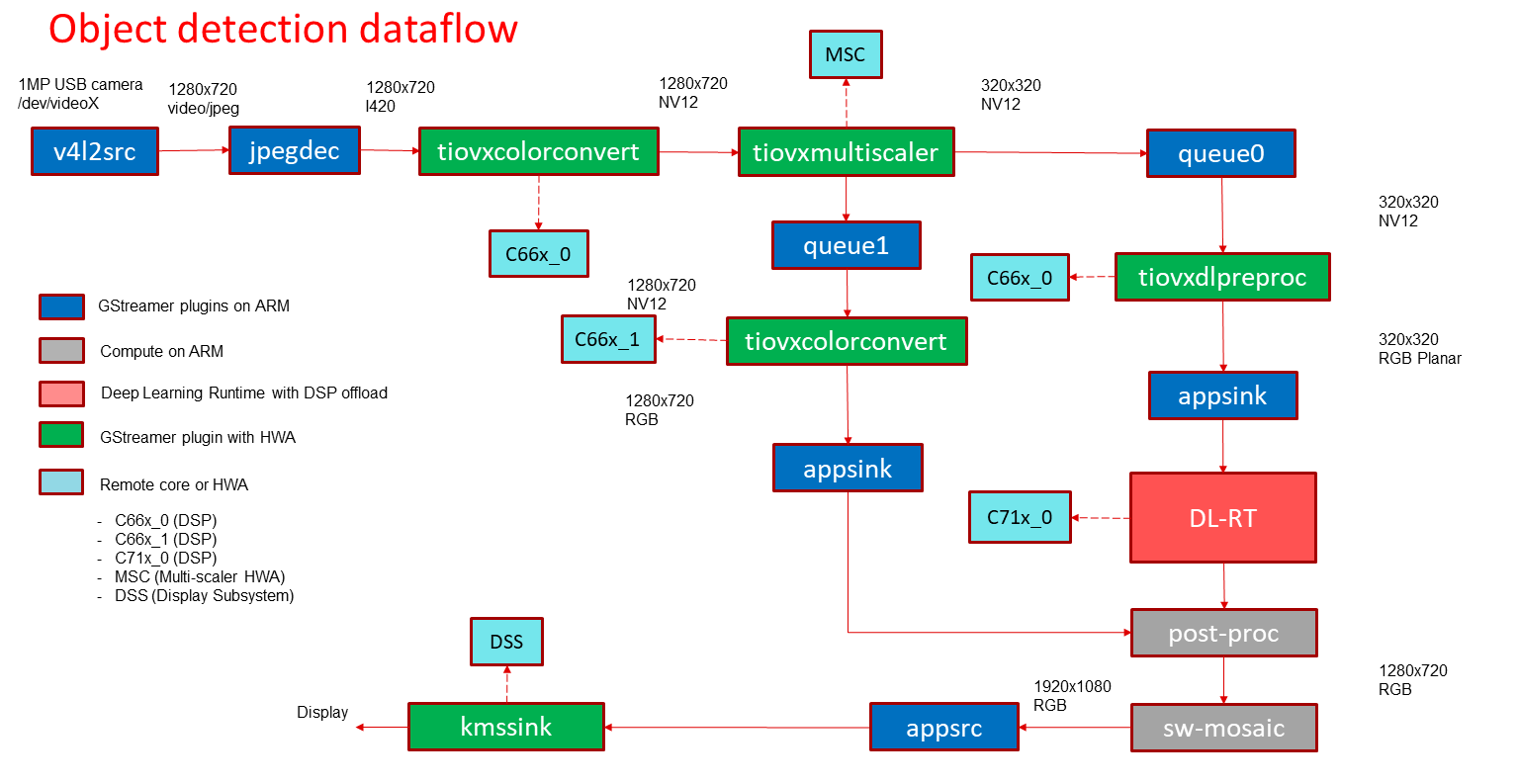
Fig. 15 GStreamer based data-flow pipeline for object detection demo with USB camera and display¶
Semantic Segmentation¶
In this demo, a frame is grabbed from an input source and split into two paths. The “analytics” path resize the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The “visualization” path is provided to the post-processing module which blends each segmented pixel to a color map. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
v4l2src device=/dev/video2 io-mode=2 ! image/jpeg, width=1280, height=720 ! jpegdec ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=512, height=512 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=0 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.016000 scale-1=0.016000 scale-2=0.016000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=1280, height=720 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
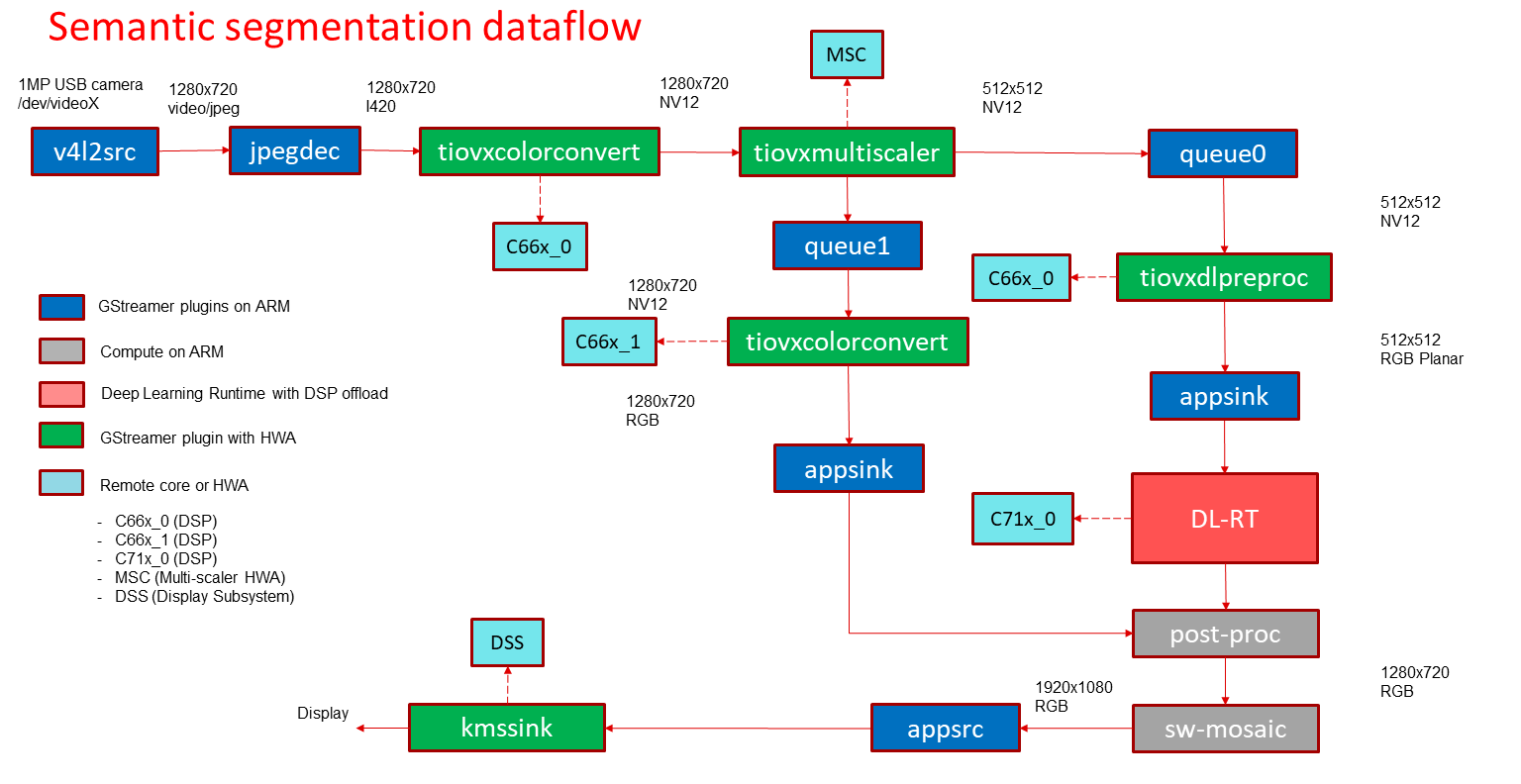
Fig. 16 GStreamer based data-flow pipeline for semantic segmentation demo with USB camera and display¶
Video source¶
In this demo, a video file is read from a known location and passed to a de-muxer to extract audio and video streams, the video stream is parsed and raw encoded information is passed to a video decoder and the resulting output is split into two paths. The “analytics” path resizes the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The “visualization” path is provided to the post-processing module which blends each segmented pixel to a color map. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
filesrc location=/opt/edge_ai_apps/data/videos/video_0000.mp4 ! qtdemux ! h264parse ! v4l2h264dec ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=320, height=320 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=1280, height=720 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
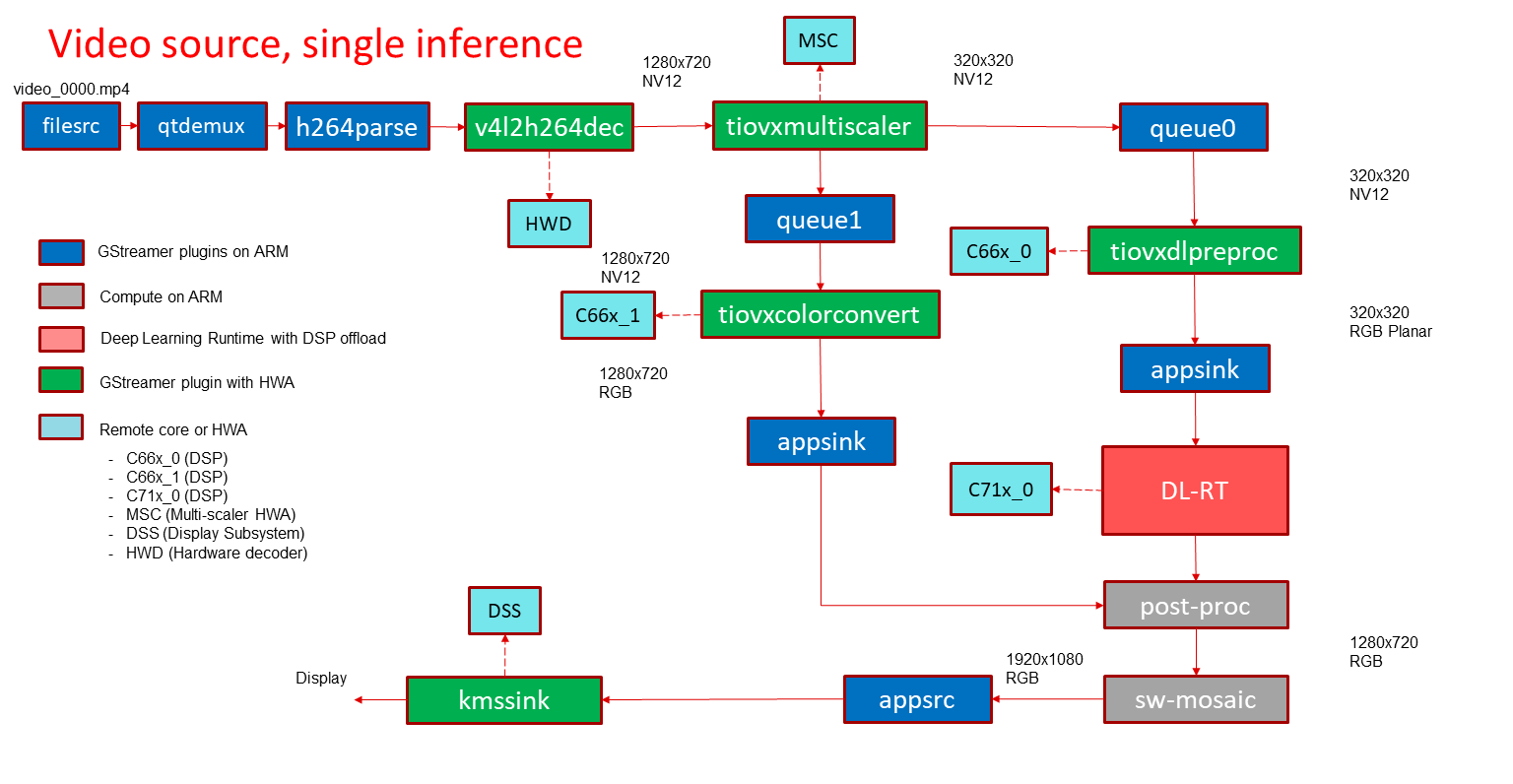
Fig. 17 GStreamer based data-flow pipeline with video file input source and display¶
RTSP source¶
In this demo, a video file is read from a RTSP source and passed to a de-muxer to extract audio and video streams, the video stream is parsed and raw encoded information is passed to a video decoder and the resulting output is split into two paths. The “analytics” path resizes the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The “visualization” path is provided to the post-processing module which blends each segmented pixel to a color map. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
rtspsrc location=rtsp://<ip-addr>:<port>/<location> latency=0 buffer-mode=auto ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! v4l2h264dec ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=320, height=320 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=1280, height=720 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
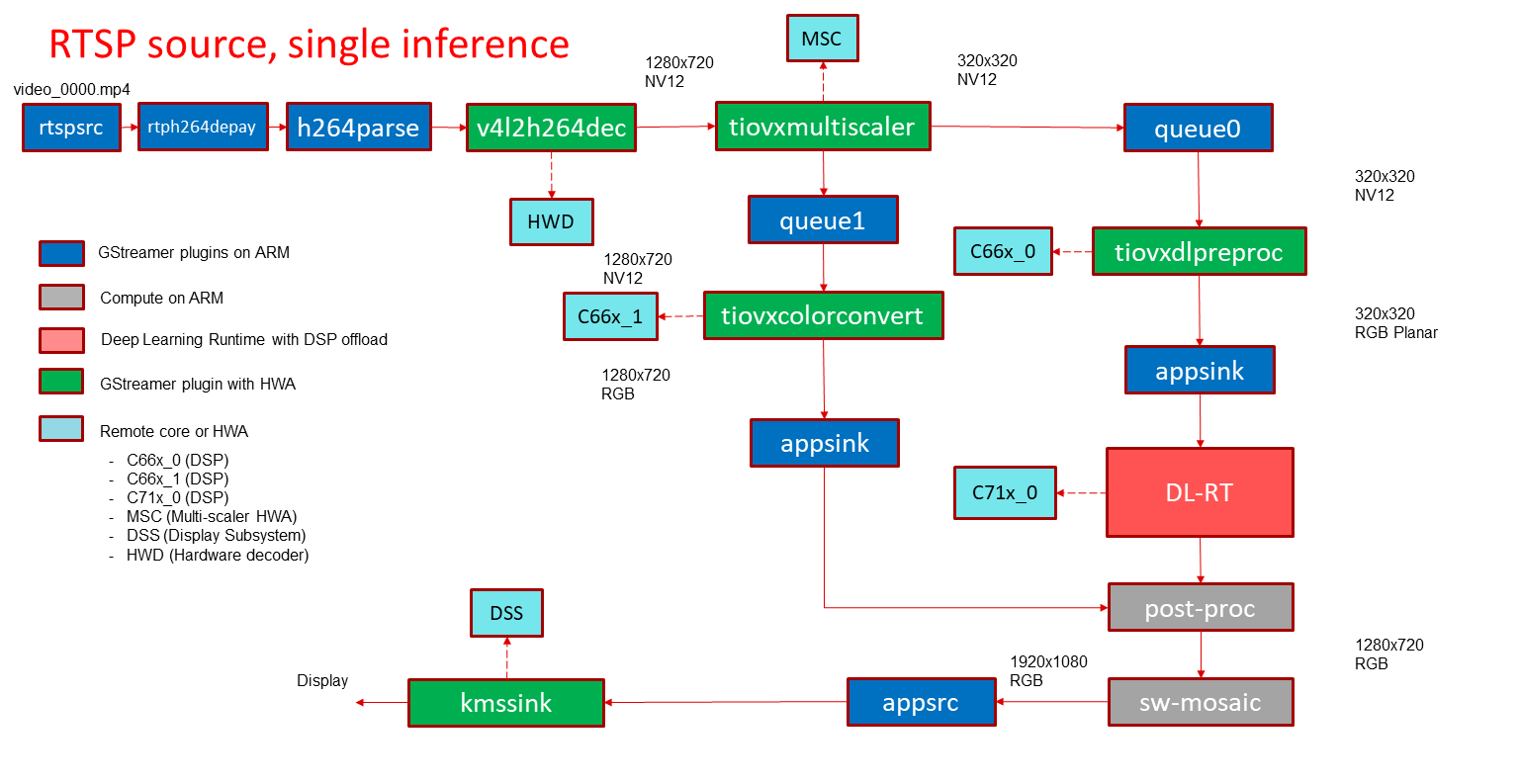
Fig. 18 GStreamer based data-flow pipeline with RTSP based video file source and display¶
Single Input Multi Instance¶
In this demo, a frame is grabbed from an input source and split into multiple paths. Each path is further split into two sub-paths one for analytics and another for visualization. Each path can run any type of network, image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation and using any supported run-time.
For example the below GStreamer pipeline splits the input into 4 paths for running 4 deep learning networks. First is a semantic segmentation network, followed by object detection network, followed by two image classification networks. If we look at the image classification path, the analytics sub-path resizes the input to maintain the aspect ratio and crops the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The visualization sub-path is provided to the post-processing module which overlays the detected classes. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
v4l2src device=/dev/video2 io-mode=2 ! image/jpeg, width=1280, height=720 ! jpegdec ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tee name=tee_split0
tee_split0. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
tee_split0. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_02
tee_split0. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_03
tee_split0. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_04
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=512, height=512 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=0 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.016000 scale-1=0.016000 scale-2=0.016000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_02. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=320, height=320 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_1 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_02. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_1 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_03. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=454, height=256 ! tiovxcolorconvert out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! videobox left=115 right=115 top=16 bottom=16 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_2 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_03. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_2 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_04. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=454, height=256 ! tiovxcolorconvert out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! videobox left=115 right=115 top=16 bottom=16 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=0 mean-0=123.675000 mean-1=116.280000 mean-2=103.530000 scale-0=0.017000 scale-1=0.018000 scale-2=0.017000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_3 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_04. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_3 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
Multi Input Multi Instance¶
In this demo, a frame is grabbed from multiple input sources and split into multiple paths. The multiple input sources could be either multiple cameras or a combination of camera, video, image, RTSP source. Each path is further split into two sub-paths one for analytics and another for visualization. Each path can run any type of network, image classification, object detection, semantic segmentation and using any supported run-time.
For example the below GStreamer pipeline splits two inputs into 4 paths for running 2 deep learning networks. First is a object detection network, followed by image classification networks. If we look at the image classification path, the analytics sub-path resizes the input to maintain the aspect ratio and crops the input to match the resolution required to run the deep learning network. The visualization sub-path is provided to the post-processing module which overlays the detected classes. The software mosaic step is used to position and size the output window on an empty background before sending to display.
GStreamer input pipeline:
v4l2src device=/dev/video2 io-mode=2 ! image/jpeg, width=1280, height=720 ! jpegdec ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tee name=tee_split0
tee_split0. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_01
tee_split0. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_02
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=320, height=320 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_01. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_0 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_02. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=454, height=256 ! tiovxcolorconvert out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! videobox left=115 right=115 top=16 bottom=16 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=1 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.008000 scale-1=0.008000 scale-2=0.008000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_1 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_02. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_1 drop=true max-buffers=2
filesrc location=/opt/edge_ai_apps/data/videos/video_0000.mp4 ! qtdemux ! h264parse ! v4l2h264dec ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tiovxcolorconvert ! video/x-raw, format=NV12 ! tee name=tee_split1
tee_split1. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_11
tee_split1. ! queue ! tiovxmultiscaler name=split_12
split_11. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=512, height=512 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=0 mean-0=128.000000 mean-1=128.000000 mean-2=128.000000 scale-0=0.016000 scale-1=0.016000 scale-2=0.016000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_2 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_11. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_2 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_12. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=454, height=256 ! tiovxcolorconvert out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! videobox left=115 right=115 top=16 bottom=16 ! tiovxdlpreproc data-type=10 channel-order=0 mean-0=123.675000 mean-1=116.280000 mean-2=103.530000 scale-0=0.017000 scale-1=0.018000 scale-2=0.017000 tensor-format=rgb out-pool-size=4 ! application/x-tensor-tiovx ! appsink name=pre_3 drop=true max-buffers=2
split_12. ! queue ! video/x-raw, width=640, height=360 ! tiovxcolorconvert target=1 out-pool-size=4 ! video/x-raw, format=RGB ! appsink name=sen_3 drop=true max-buffers=2
GStreamer output pipeline:
appsrc format=GST_FORMAT_TIME is-live=true block=true do-timestamp=true name=sink_0 ! kmssink sync=false driver-name=tidss
