3.2. Boot Monitor¶
3.2.1. Boot Monitor User’s Guide¶
Overview
The Boot Monitor software provides secure privilege level execution service for Linux kernel code through SMC calls. It only applies to the following Keystone-2 platforms:
- 66AK2H EVM
- K2E EVM
- XTCIEVMK2X EVM
- TCIEVMK2L EVM
- K2G EVM
ARM cortex A15 requires certain functions to be executed in the PL1 privilege level. Boot monitor code provides this service. A high level architecture of the boot monitor software is shown below
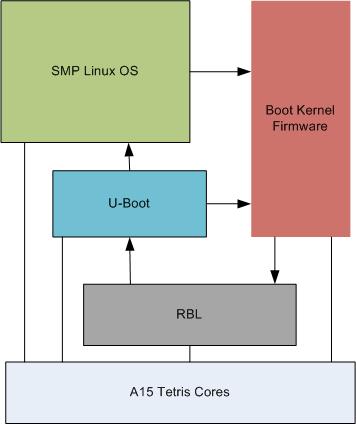
Boot monitor code is built as a standalone image and is loaded into Keystone-2 at the top 64K of the MSMC SRAM memory. That is,
at 0x0C5F 0000 for K2HK at 0x0C14 0000 for K2E/L at 0x0C04 0000 for K2G
The image has to be loaded to the above address through tftp or other means. It gets initialized through the u-boot command install_skern. The command takes the load address above as the argument.
This wiki will cover the basic steps for building boot monitor.
General Information
Getting the Boot Monitor Source Code
The easiest way to get access to the boot monitor source code is by downloading and installing the Processor SDK Linux. Once installed, the boto monitor source code is included in the SDK’s board-support directory.
Building Boot Monitor
Setting the tool chain path
$ PATH=<ProcSDK_Install_dir>/linux-devkit/sysroots/x86_64-arago-linux/usr/bin:$PATH
The command to clean the boot monitor
$ make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- clean
The command to build the boot monitor
$ make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- [image_<ks2_platform>]
where ks2_platform = k2hk, k2e, k2l, or k2g
if image_<ks2_platform> is left blank, all platforms will be built.
Boot sequence of primary core
In the primary ARM core, ROM boot loader (RBL) code is run on Power on reset. After completing its task, RBL load and run u-boot code in the non secure mode. Boot monitor gets install through the command mon_install(). As part of this following will happen
- boot monitor primary core entry point is entered via the branch address where it was installed
- As part of non secure entry, boot monitor calls the RBL API (smc #0) through SMC call passing the _skern_init() as the argument. This function get called as part of the RBL code
- _skern_init() assembly function copies the RBL stack to its own stack. It initializes the monitor vector and SP to point to its own values. It then calls skern_init() C function to initialize to do Core or CPU specific initialization. r0 points to where it enters from primary core or secondary core, r1 points to the Tetris PSC base address and r2 points to the ARM Arch timer clock rate. RBL enters this code in monitor mode. skern_init() does the following:
- Initialize the arch timer CNTFREQ
- Set the secondary core entry point address in the ARM magic address for each core
- Configure GIC controller to route IPC interrupts
Finally the control returns to RBL and back to non secure primary core boot monitor entry code.
- On the primary core, booting of Linux kernel happens as usual through the bootm command.
- At Linux start up, primary core make smc call to power on each of the secondary core. smc call is issued with r0 pointing to the command (0 - power ON). r1 points to the CPU number and r2 to secondary core kernel entry point address. Primary core wait for secondary cores to boot up and then proceeds to rest of booting sequence.
Boot sequence of secondary core
At the secondary core, following squence happens
- On power ON reset, RBL initializes. It then enters the secondary entry point address (_skern_123_init()) of the boot monitor core which was written to the fast boot address in RBL by the primary core. The init code sets its own stack, and vectors. It then calls skern_123_init() C function to initialize per CPU variables. It initializes the arch timer CNTFREQ to desired value.
- On return from skern_123_init(), it returns the secondary core kernel entry point address, and back to _skern_123_init() which goes to non-secure SVR mode and jumps to the secondary kernel entry point address, and it starts booting secondary instance of Linux kernel.
3.2.2. Boot Monitor Release Notes¶
Build Information
