3.2.2.7. HSR Offload¶
Introduction
HSR framework in linux allows offloading below functionalities to the device hsr-fwd-offload: For forwarding HSR frames one port to another i.e port-to-port forwarding
hsr-dup-offload: Duplicate the outgoing HSR frame
The ICSSG HSR firmware supports port-to-port forwarding, Tx packet duplication and this allows to offload these capabilities from HSR driver in software to the PRU-ICSSG.
To enable offloading using below commands To enable port-to-port offload
ethtool -K <interface> hsr-fwd-offload on
To enable Tx packet duplication
ethtool -K <interface> hsr-fwd-offload on
ethtool -K <interface> hsr-dup-offload on
Note
The ICSSG HSR firmware is designed to always carry out port-to-port forwarding. So whenever any of the HSR features are to be offloaded, the port-to-port forwarding must also be offloaded. It is not possible to offload only Tx packet duplication functionality.
The below script sets up an HSR interface with the port-to-port forwarding and Tx packet duplication offloaded
#!/bin/sh
#For non offload - sh hsr_setup.sh hsr_sw <INTF_A> <INTF_B> <HSR_INTF_IP_ADDR>
#For offload - sh hsr_setup.sh hsr_hw <INTF_A> <INTF_B> <HSR_INTF_IP_ADDR>
if [ "$#" != "4" ]
then
echo "$0 <hsr_sw/hsr_hw> <intf1> <intf2> <ip addr>"
exit
fi
if [ "$1" != "hsr_sw" ] && [ "$1" != "hsr_hw" ]
then
echo "$0 <hsr_sw|hsr_hw>"
exit
fi
if=hsr0
ifa=$2
ifb=$3
ip=$4
mac=`ifconfig $ifa | grep ether | cut -d " " -f 10`
device="platform/"
device+=`dmesg | grep $ifa | grep icssg-prueth | grep -m 1 "Link is Up" | awk '{print $4}'`
echo "ip=$ip"
echo "if=$if"
echo "mac=$mac"
echo "slave-a=$ifa"
echo "slave-b=$ifb"
echo "device=$device"
ip link delete hsr0 2> /dev/null
ip link set $ifa down
ip link set $ifb down
sleep 1
if [ "$1" == "hsr_hw" ]
then
ethtool -k $ifa | grep hsr
ethtool -K $ifa hsr-fwd-offload on
ethtool -K $ifa hsr-dup-offload on
ethtool -k $ifa | grep hsr
ethtool -k $ifb | grep hsr
ethtool -K $ifb hsr-fwd-offload on
ethtool -K $ifb hsr-dup-offload on
ethtool -k $ifb | grep hsr
devlink dev param set $device name hsr_offload_mode value true cmode runtime
fi
ip link set dev $ifa address $mac
ip link set dev $ifb address $mac
ip link set $ifa up
sleep 1
ip link set $ifb up
sleep 1
ip link add name $if type hsr slave1 $ifa slave2 $ifb supervision 45 version 1
sleep 3
ip addr add $ip/24 dev $if
ip link set $if up
To create HSR interface with IP address 192.168.2.20 using eth1 and eth2, run the script by passing the arguments as below
sh hsr_setup.sh hsr_hw eth1 eth2 192.168.2.20
Multicast Filtering
All multi-cast addresses not registered will be filtered out.
Multicast Add/Delete
Multicast MAC address can be added/deleted using ip maddr commands or Linux socket ioctl SIOCADDMULTI/SIOCDELMULTI.
Show muliticast address
Show current list of multicast address for the HSR interface
ip maddr show dev <hsr_intf>
Example:
# ip maddr show dev hsr0
7: hsr0
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 3
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc users 3
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 3
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 3
inet 224.0.0.252
inet 224.0.0.251
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1
inet6 ff01::1
Add muliticast address
Add a multicast address
ip maddr add <multicast_mac_addr> dev <hsr_intf>
Example: To add a multicast address and display the list in HSR and slave ports
# ip maddr add 01:80:c4:00:00:0e dev hsr0
# ip maddr show dev hsr0
7: hsr0
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 3
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc users 3
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 3
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 3
link 01:80:c4:00:00:0e users 3 static
inet 224.0.0.252
inet 224.0.0.251
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1
inet6 ff01::1
# ip maddr show dev eth1
5: eth1
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 2
link 01:80:c2:00:00:00
link 01:80:c2:00:00:03
link 01:80:c2:00:00:0e
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 2
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 2
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc
link 01:80:c4:00:00:0e
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1 users 2
inet6 ff01::1
# ip maddr show dev eth2
6: eth2
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 2
link 01:80:c2:00:00:00
link 01:80:c2:00:00:03
link 01:80:c2:00:00:0e
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 2
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 2
link 01:80:c4:00:00:0e
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1 users 2
inet6 ff01::1
Delete muliticast address
Delete a multicast address
ip maddr del <multicast_mac_addr> dev <hsr_intf>
Example: To delete an added multicast address and dislay the list of HSR and slave intefaces.
# ip maddr del 01:80:c4:00:00:0e dev hsr0
# ip maddr show dev hsr0
7: hsr0
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 3
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb users 3
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc users 3
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 3
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 3
inet 224.0.0.252
inet 224.0.0.251
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1
inet6 ff01::1
# ip maddr show dev eth1
5: eth1
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 2
link 01:80:c2:00:00:00
link 01:80:c2:00:00:03
link 01:80:c2:00:00:0e
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 2
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 2
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1 users 2
inet6 ff01::1
# ip maddr show dev eth2
6: eth2
link 01:00:5e:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:00:00:00:01 users 2
link 33:33:ff:1e:e8:10 users 2
link 01:80:c2:00:00:00
link 01:80:c2:00:00:03
link 01:80:c2:00:00:0e
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fb
link 01:00:5e:00:00:fc
link 33:33:00:00:00:fb users 2
link 33:33:00:01:00:03 users 2
inet 224.0.0.1
inet6 ff02::1:3
inet6 ff02::fb
inet6 ff02::1:ff1e:e810
inet6 ff02::1 users 2
inet6 ff01::1
Performance
This section describes the throughput and CPU usage metrics in the offload case
Setup
A sample test setup is as show below
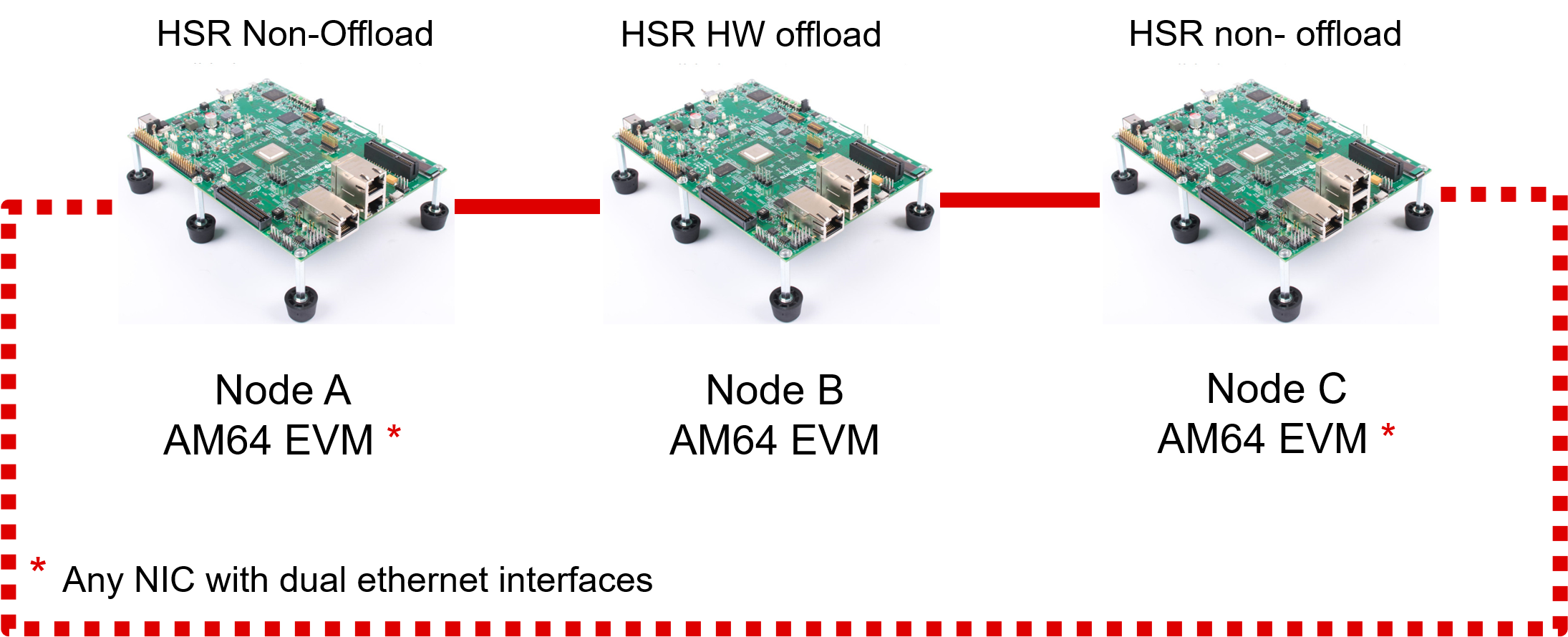
Test Procedure
1. Connect the LAN cables between the DANH as shown in the Section 1
2. Execute the commands to setup and create HSR interface
a. To setup HSR non-offload on Node A and Node C,
sh hsr_setup.sh hsr_sw <INTF_A> <INTF_B> <HSR_INTF_IP_ADDR>
b. To Setup HSR offload on Node B,
sh hsr_setup.sh hsr_hw <INTF_A> <INTF_B> <HSR_INTF_IP_ADDR>
3. Confirm ping across all Nodes
a. Node A < - - > Node B
b. Node B < - - > Node C
c. Node C < - - > Node A
4. Disconnect the LAN cable between Node A and Node C
5. Monitor the CPU usage on Node B
mpstat -P ALL 1
6. Run iperf3 server on Node C
iperf3 -s -i 1
7. Run iperf3 client on Node A for 60 secs
iperf3 -c -1 -t 60 <Node_C_IP_Addr>
CPU Usage on Node B
CPU usage at Node B found to be negligible
** Snippet from the continuous stats **
CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
all 0.00 0.00 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 99.50
0 0.00 0.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 99.00
1 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %idle
all 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 99.50
0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
1 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
Througput at Node A
Sender |
Receiver |
475 Mbits/sec |
475 Mbits/sec |
