 |
PDK API Guide for J721E
|
 |
PDK API Guide for J721E
|
The Unified Ethernet Low-Level Driver (Enet LLD) is a PDK driver that aims at providing an unified interface for the different Ethernet peripherals found in TI SoCs.
The Enet LLD is composed of the following layers: top-layer APIs, peripheral layer, module layer and CSL. The diagram below depicts the layers in the Enet LLD.
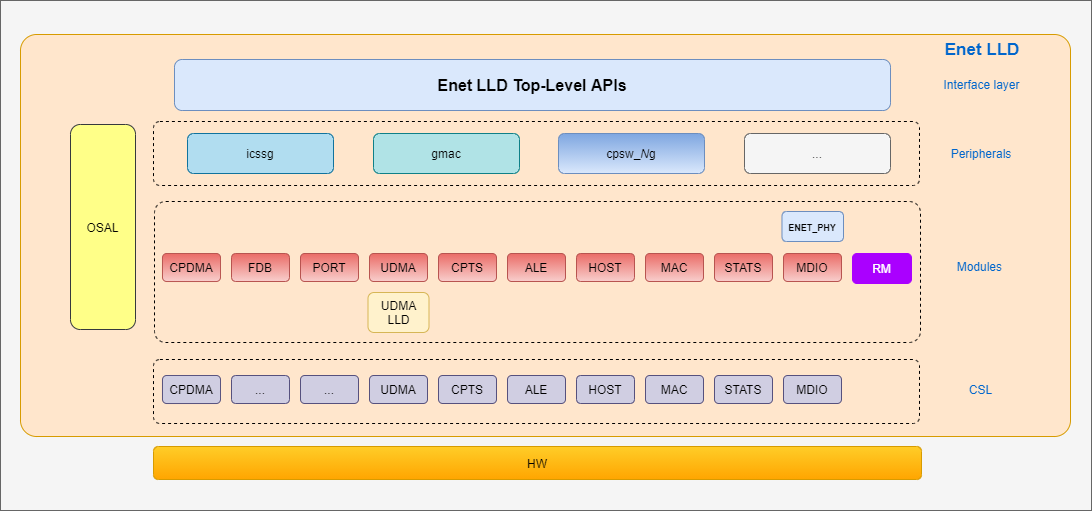
The Enet LLD provides two sets of APIs: control and DMA.
The control API is an IOCTL-based interface which is used by applications to control the Ethernet peripheral and its submodules.
For further details on the top-level control APIs, refer to the Enet Main API.
The DMA API is used by applications to perform data movement related operations, such as opening and closing DMA channels, submitting and retrieving packets from the underlying DMA controller.
For further details on the top-level control APIs, refer to the Enet Data Path (DMA).
The following diagram shows the usage of Enet LLD top-level APIs by local and remote clients.

Enet LLD supports only CPSW families of Ethernet devices. ICSSG is not supported.
Jacinto 7 family devices offer networking functionality through the Gigabit Ethernet MAC (MCU_CPSW0) and the Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW0) subsystems. They provide Ethernet packet communication between the connected port(s) and the System on Chip. The total number of ports include host port which is an internal port providing the packet streaming interface to the device internal cores. The external ports are MAC ports supporting Media Independent Interface (MII) like MII, Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII), Reduced Media Independent Interface (RMII), Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface (RGMII), Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface (SGMII) and Quad Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface (QSGMII). The MII modes supported vary based on device variant.
MCU_CPSW0 is a two-port CPSW switch instance: one MAC port and a CPPI DMA host port. It's commonly referred to as CPSW2G.
CPSW0 is an integrated Ethernet switch IP with nine-port: eight MAC ports and a CPPI DMA host port. This CPSW instance is referred to as CPSW9G throughout most documentation and code. The CPSW9G switch facilitates the transfer of data between external ports along with internal traffic. Any core of Jacinto 7 devices can transmit/receive data to/from the switch.
CPSW9G is a shared resource and the Ethernet Switch Firmware is the software running on Main domain R5F of Jacinto 7, used for configuration, coordination and management of CPSW9G resources between internal processing cores and external ports. The Ethernet Switch Firmware software is mainly based on the PDK Enet low-level driver (Enet LLD), but also relies on other PDK drivers like UDMA for data transfers to the internal processing cores.
The diagram below show the comparison of a typical automotive system using an external switch and an MCU, with a similar system on Jacinto 7 with integrated Ethernet switch.

The following diagram shows an example of the Enet LLD integration in a J721E device of the Jacinto 7 family. In this integration example, the Ethernet Firmware is built on top of the Enet LLD which provides an abstraction to the underlying functionality of the ENET_CPSW_9G Ethernet peripheral.

| Revision | Date | Author | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 17 Aug 2020 | Misael Lopez | First version | Draft |