Texas Instruments F29x UART Flash Programmer CLI Example Package
Located in F29H85X-SDK /flash_programmers/uart_flash_programmer
This page provides a brief rundown of the F29x UART Flash Programmer.
The UART Flash Programmer is a command-line interface (CLI) tool that runs on a PC and communicates with an F29x device via UART. It can be used to load firmware1 via UART boot mode. It can also communicate with a UART secondary bootloader (SBL) running on the device to perform more advanced operations, such as programming the device's flash memory. See RAM-based UART SBL and Flash-based UART SBL for more detail.
The Flash Programmer CLI is supported on Windows and Linux operating systems. Precompiled executables are included for Windows, and a CMake build script is provided for Linux.
1. In HS-FS (High Security - Field Securable) state, boot authorization is disabled, and a special mode called RAMOPEN is enforced, which prevents instructions from executing in flash. Therefore, RAM-based SBL is used for peripheral boot to receive and execute Flash Programmer commands.
- For more information, please see the "RAMOPEN Feature" of the ROM section in the F29H85x Technical Reference Manual (TRM).
Two methods are provided to compile the source code found under /src directory:
uart_flash_programmer.sln into Visual Studio and build the project.build_cmake.sh to automate CMake buildchmod +x build_cmake.sh && ./build_cmake.shmkdir build && cd buildcmake -S .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE={Debug/Release}cmake --build .Two versions of the precompiled Windows executable are provided for this example:
--boot-only parameter can be added to only load the SBL in UART boot and exit.ENABLE_PERIPHERAL_BOOT in include/Common.hF29H85x device progress through a lifecycle defined by their security state. The following table lists the MCU device types (also known as device lifecycles) and their corresponding security policies:
| F29x Device Type | |
|---|---|
| HS-FS (High Security - Field Securable) | • No authentication on device boot • No device security features are enforced except load HSM auth • No SSU Security Configuration protection |
| HS-KP (High Security - Key Provisioned) | • Requires authentication on device boot • Device security features are enforced • SSU security configuration are cleared and uses default settings • A temporary state prior to HS-SE |
| HS-SE (High Security - Security Enforced) | • Requires authentication on device boot • Device security features are enforced • SSU security configuration are configured and is protected by HSM2 • Secure boot enabled and Root-of-Trust on user key |
2. While the Hardware Security Module (HSM) is independent of the Safety and Security Unit (SSU), which governs the C29x CPU and memory security model via its security configuration, the HSM does validate and protect the Security Configuration when device security features are enabled.
For more information. Refer to the SSU section of the F29H85x TRM.
By default, any out-of-the-box device is in the HS-FS state. This indicates that the device comes with the manufacturer's key, and no HSM security features are enforced. In the HS-FS state, the CPU is permitted to directly program its flash banks without the HSM, and is denoted as unsecure programming.
Device conversion from HS-FS to HS-SE is performed through provisioning, two operations must be conducted:
The first operation is known as Key Provisioning (KP), which converts an HS-FS device into a temporary HS-KP state.
The second operation is part of Code Provisioning (CP), which converts an HS-KP device into an HS-SE device with full device, CPU, and memory security enabled.
Key Provision (HS-FS to HS-KP):
During Key Provisioning, the user can replace the TI-provided key with a custom private key via OTP Keywriter service. Once a new custom key is provisioned successfully, the device converts to the HS-KP state after a power-on reset (PORSn). Authentication is now enforced, and the user must supply the correct X.509 certificate-appended binary images, security configurations, or keys to pass authentication for future operations.
Code Provision (HS-KP/SE to HS-SE):
Code Provisioning encompasses the secure flashing of the Sec Cfg, CPU flash, and HSM flash, all of which require HSM authentication and validation. In the HS-KP state, successfully programming the Security Configuration will convert the device to HS-SE after a power-on reset (PORSn). Although the order of flashing operations is not strictly enforced, it is recommended to flash the Sec Cfg first, followed by the HSM flash and then the CPU flash. Code Provisioning supports all flash bank modes.
The UART Flash Programmer CLI and RAM-based UART SBL supports Key and Code Provisioning as available options.
The following is a brief summary of the F29H85x device flash bank modes:
(For F29H85x devices with smaller flash configurations, reduce each flash size by the same ratio.)
| F29H85x Bank modes | |
|---|---|
| Mode 0 | • Bank swap disabled • CPU1 4MB flash • CPU3 flash disabled |
| Mode 1 | • Bank swap enabled • CPU1 2MB flash • CPU3 flash disabled |
| Mode 2 | • Bank swap disabled • CPU1 2MB flash • CPU3 2MB flash |
| Mode 3 | • Bank swap enabled • CPU1 1MB flash • CPU3 1MB flash |
By default, an out-of-box device is in mode 0.
Throughout various documents, these terms are used to represent different firmware upgrade terminologies. In the context of F29H85x , they are described as follows:
Device Firmware Upgrade (DFU):
Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA):
Live Firmware Upgrade (LFU):
The most relevant firmware upgrade method depends on the service model and end-user application requirements.
The UART Flash Programmer can interface with either a RAM-based or a Flash-based UART SBL. Their primary differences are outlined below:
| SBL Comparison | ||
|---|---|---|
| RAM-based UART SBL | Flash-based UART SBL | |
| Former name | Flash Kernel | Boot Manager |
| Type | Temporary, runs in RAM | Persistent, resides alongside of user application |
| Device boot | SBL loads via: • Periperial UART boot (.bin) • CCS Debug3 (.out) | SBL loads via: • Flash boot (.bin) (programmed by RAM-based SBL) • CCS Flash3 (.out) • Uniflash3(.out) |
| Which programmer to use | • uart_flash_programmer.exe • build w/ ENABLE_PERIPHERAL_BOOT | • uart_flash_programmer_appIn.exe • build w/o ENABLE_PERIPHERAL_BOOT |
| Unsecure Programming (HS-FS only) | DFU • Programs to active flash bank • supports all bankmode - 0,1,2,3 | FOTA • A/B partition, programs to dormant flash bank • supports bankmode 1 and 3 |
| Secure Programming | Secure KP & CP • Interface with OTP Keywriter • DFU in mode 0 and 2 • FOTA in mode 1 and 3 | Secure CP (HS-SE only) • FOTA |
| HSM Firmware (Pre-req for secure programming) | RAM-based HSM runtime | Flash-based HSM runtime |
| Use case | • Initial device bringup & conversion • DFU service model | • FOTA service model |
As described, the primary purpose of the RAM-based SBL is for initial device bring-up, such as supporting KP to provision private keys, which converts the device to HS-KP and subsequently to HS-SE with CP commands.
In contrast, the Flash-based SBL is programmed by the RAM-based SBL and is part of the device firmware that activates upon receiving Flash Programmer commands. Its functionality is a streamlined version of the RAM-based SBL, tailored for FOTA. It requires the RAM-based SBL to set up the appropriate bank modes and security states before the Flash-based SBL can be booted.
3. Only available in HS-FS (unsecure programming). This will not work in HS-KP or HS-SE, since boot authentication and the JTAG debug firewall are enabled by default.
The Flash Programmer is a command-line tool. Run it from a terminal with the required arugments.
Windows Example:
Linux Example:
The program can be run interactively, where it will prompt for operations and wait for user input, or in an automated mode using the --input parameter to provide a sequence of commands.
For details on peripheral boot and avilable commands, see the sections below.
To load a RAM-based SBL via device peripheral, first set the device boot pin into UART boot.
| F29H85x Default Boot Modes | ||
|---|---|---|
| Boot Mode | GPIO72 (Default boot mode select pin 1) | GPIO84 (Default boot mode select pin 2) |
| Parallel IO | 0 | 0 |
| UART | 0 | 1 |
| CAN | 1 | 0 |
| Flash | 1 | 1 |
Then reset / plug-in the device to the PC, so Boot ROM is in UART Boot. And run the UART Flash Programmer (uart_flash_programmer.exe or build with ENABLE_PERIPHERAL_BOOT).
In UART Boot, ROM will first send SoC ID strings via UART, and then waits for incoming UART data before timeout occurs(~2min) & switches to Wait Boot. Once it receives UART data, it'll echo back the data, or stops if something fails to validate. The flash programmer monitors the echo-back data and will exit with failure status if the echoed back does not match the expected data.
Therefore, if Flash Programmer receives an unmatched data and exits, simply reset the device (XRSn suffice) and retry again.
However, if a UART bootload of an image is consistently stuck (ROM stopped echoing back data which stops programmer from progressing), user can visually observe where data transfer stopped and have a clue of what happened:
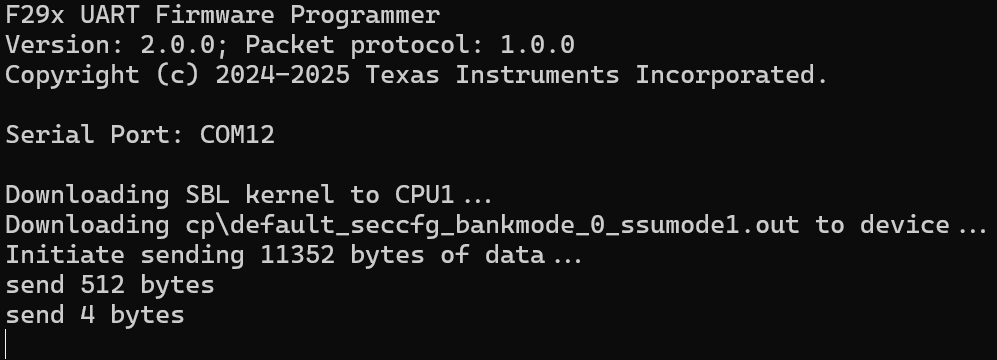
See the image above on an example of bootloading an example that has improper X.509 format.
/note Since ROM sends out SoCID string at the start of UART Boot and UART Flash Programmer monitors echo-back data for validation, while it is unlikely for a mannual run to experience the clash between the two, when automating the flow, please make sure device power-on/reset is at least 100ms apart from invoking the UART Flash Programmer for UART boot.
All application & SBL images must be in binary format and be prepended with a X.509 certificate. Even in HS-FS where authentication is disabled, the ROM and SBL still use the length field of a dummy certificate to determine how many bytes to read.
To generate the combined image with an X.509 certificate, please refer to the post-build steps in the RAM/Flash-based SBL examples. (Note that the Flash-based SBL also incorporates additional steps to combine the bootloader code and application firmware).
In addition, refer to the various signing scripts located in F29H85X-SDK /tools/boot/signing.
Supply -h or –help as a parameter will prompt the following message:
F29x UART Firmware Programmer
Supported parameters are:
-d, --device <device> - The device family of the target device:
(f29h85x, f29p58x, f29p32x)
-p, --port <port> - Serial COM/tty port used for UART communication.
(port format: COM<num>, /dev/ttyUSB<num>, /dev/ttyACM<num>)
-k, --kernel <file> - File path for ram-based sbl (formerly flash kernel)
-a1, --appcpu1 <file> - File path for Flash-based C29 CPU1 application image (HS-FS Only)
-a3, --appcpu3 <file> - File path for Flash-based C29 CPU3 application image (HS-FS Only)
-sr, --hsmrt <file> - File path for RAM-based HSM runtime (HSMRt) image (Prerequisite for KP & CP)
-sk, --hsmkeys <file> - File path for HSM keys image (HS-KP key provision)
-s1, --cpappcpu1 <file> - File path for Flash-based C29 CPU1 application image (HS-SE code provision)
-s3, --cpappcpu3 <file> - File path for Flash-based C29 CPU3 application image (HS-SE code provision)
-sh, --cpapphsm <file> - File path for Flash-based HSM application image (HS-SE code provision)
-sc, --cpseccfg <file> - File path for Sec Cfg program image (HS-SE code provision)
-e1, --entryaddr <hex_num> - (optional) Override entry address of the C29 CPU1 application
-tb, --targetbaud <dec_num> - (optional) Propose the specified UART baudrate amongst target & host when reconfiguring UART (automatic in non-appIn). If not set, by default the target-proposed baudrate would be used.
-hb, --hostbaud <dec_num> - (appIn ONLY) Configures host with the alternate UART baudrate. Use this param when target's baudrate is different than the default baudrate (BootROM's UART boot baudrate).
Note: -d, -p are mandatory parameters. -k is mandatory in non-appIn
Images must be in binary format and includes an X.509 certificate.
-i, --input <,> - Provide command input options via parameter rather than keyboard input to the console
(format: comma-separated values <num,num>, for example "--input 3,4,11,15")
--boot-only - Only do peripheral boot and exits the program right after. Can be used to load any SBL without programmer's packet protocol support.
-h, --help - Show this help.
-l, --log <file> - Log mode. Redirect all non-essential printouts to the specified file, will override -q mode
-q, --quiet - Quiet mode. Suppress all non-essential printouts
-w - Wait on keypress before exiting
--version - Display version information
Syntax: -d f29h85x -p COM41 -k ram_based_uart_sbl.bin --appcpu1 c29_cpu1_application.bin --entryaddr 10001000 --hsmrt HSM_runtimeImage.bin --hsmkeys HSM_customKeyCert.bin --cpseccfg sec_cfg_cert.bin --cpappcpu1 c29_cpu1_application.bin -cpapphsm hsm_application.bin -l output.log
When running the program, after the peripheral UART boot (if applicable) , the user will be prompted with the following options:
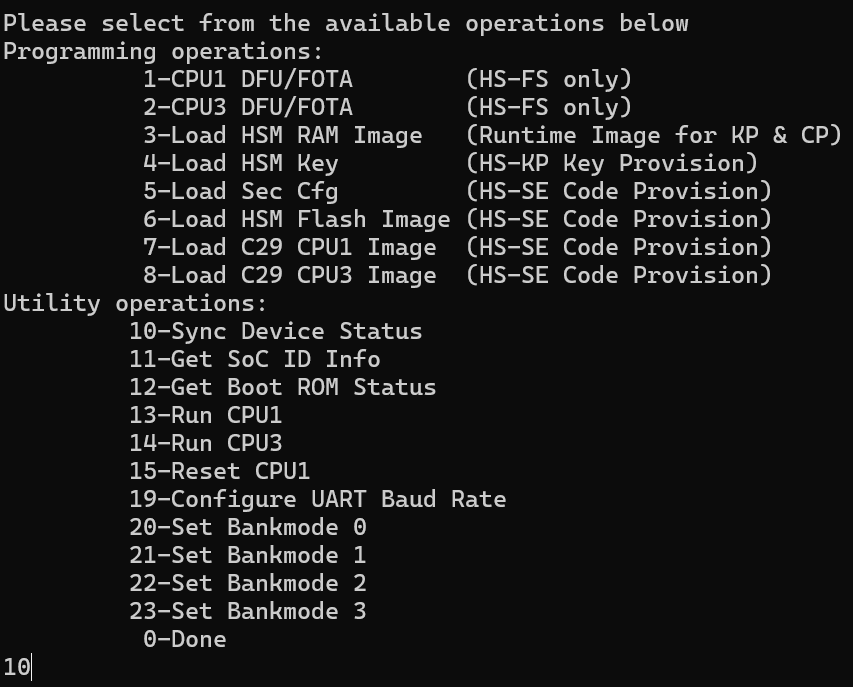
Programming Commands:
Utility Commands:
Shown below lists all the software revision history for the uart flash programmer:
| Software Version | SDK Release | Changelog |
|---|---|---|
| v1.00.00 | 1.00.00.00 | First release, in F29H85X-SDK |
| v1.01.00 | 1.01.00.00 | Enhancements:
|
| v2.00.00 | 1.02.01.00 | Enhancements:
|
For additional help and support, please visit E2E™ design support forum